S&P_500
S&P 500
American stock market index
The Standard and Poor's 500, or simply the S&P 500,[4] is a stock market index tracking the stock performance of 500 of the largest companies listed on stock exchanges in the United States. It is one of the most commonly followed equity indices and includes approximately 80% of the total market capitalization of U.S. public companies, with an aggregate market cap of more than $43 trillion as of January 2024.[2][5]
This article needs to be updated. (November 2023) |
S&P 500 Index from 1970 to 2023 | |
| Foundation | March 4, 1957; 67 years ago (1957-03-04)[1] |
|---|---|
| Operator | S&P Dow Jones Indices[2] |
| Exchanges | |
| Trading symbol |
|
| Constituents | 503[2] |
| Type | Large-cap[2] |
| Market cap | US$42.0 trillion (as of December 31, 2023) |
| Weighting method | Free-float capitalization-weighted[3] |
| Related indices | |
| Website | spglobal.com/sp-500 |

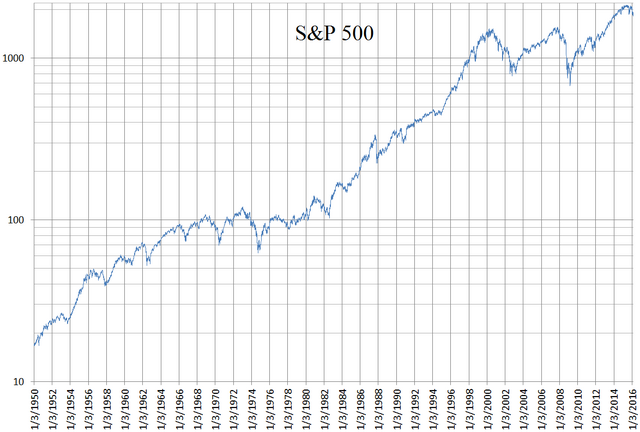


The S&P 500 index is a free-float weighted/capitalization-weighted index. As of December 29, 2023, the nine largest companies on the list of S&P 500 companies accounted for 30.9% of the market capitalization of the index and were, in order of highest to lowest weighting: Apple, Microsoft, Amazon.com, Nvidia, Alphabet (including both class A & C shares), Meta Platforms, Tesla, Berkshire Hathaway and JPMorgan Chase.[6] The components that have increased their dividends in 25 consecutive years are known as the S&P 500 Dividend Aristocrats.[7]
The index is one of the factors in computation of the Conference Board Leading Economic Index, used to forecast the direction of the economy.[8] The index is associated with many ticker symbols, including ^GSPC,[9] INX,[10] and $SPX, depending on market or website.[11] The S&P 500 is maintained by S&P Dow Jones Indices, a joint venture majority-owned by S&P Global, and its components are selected by a committee.[12][13]
Mutual and exchange-traded funds
Index funds, including mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs), can replicate, before fees and expenses, the performance of the index by holding the same stocks as the index in the same proportions. ETFs that replicate the performance of the index are issued by The Vanguard Group (NYSE Arca: VOO), iShares (NYSE Arca: IVV), and State Street Corporation (NYSE Arca: SPY and NYSE Arca: SPLG). The most liquid based on average daily volume is (NYSE Arca: SPY), although SPY has a higher annual expense ratio of 0.09% compared to 0.03% for VOO and IVV, and 0.02% for SPLG. Mutual funds that track the index are offered by Fidelity Investments, T. Rowe Price, and Charles Schwab Corporation.[14][15]
Direxion offers leveraged ETFs which attempt to produce three times the daily return of either investing in (NYSE Arca: SPXL) or shorting (NYSE Arca: SPXS) the S&P 500 index.[16] ProShares offers 2x daily return (NYSE Arca: SSO) and 3x daily return (NYSE Arca: UPRO).
Derivatives
In the derivatives market, the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) offers futures contracts that track the index and trade on the exchange floor in an open outcry auction, or on CME's Globex platform, and are the exchange's most popular product. The Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) offers options on the S&P 500 index as well as on S&P 500 index ETFs, inverse ETFs, and leveraged ETFs.
In 1860, Henry Varnum Poor formed Poor's Publishing, which published an investor's guide to the railroad industry.[17] In 1923, Standard Statistics Company (founded in 1906 as the Standard Statistics Bureau) began rating mortgage bonds[17] and developed its first stock market index consisting of the stocks of 233 U.S. companies, computed weekly.[1] Three years later, it developed a 90-stock index, computed daily.[1] In 1941, Poor's Publishing merged with Standard Statistics Company to form Standard & Poor's.[17][18]
On Monday, March 4, 1957, the index was expanded to its current 500 companies and was renamed the S&P 500 Stock Composite Index.[1] In 1962, Ultronic Systems became the compiler of the S&P indices including the S&P 500 Stock Composite Index, the 425 Stock Industrial Index, the 50 Stock Utility Index, and the 25 Stock Rail Index.[19] On August 31, 1976, The Vanguard Group offered the first mutual fund to retail investors that tracked the index.[1] On April 21, 1982, the Chicago Mercantile Exchange began trading futures based on the index.[1] On July 1, 1983, Chicago Board Options Exchange began trading options based on the index.[1] Beginning in 1986, the index value was updated every 15 seconds, or 1,559 times per trading day, with price updates disseminated by Reuters.[20]
On January 22, 1993, the Standard & Poor's Depositary Receipts exchange-traded fund issued by State Street Corporation began trading.[1] On September 9, 1997, CME Group introduced the S&P E-mini futures contract.[1] In 2005, the index transitioned to a public float-adjusted capitalization-weighting.[21] Friday, September 17, 2021, was the final trading date for the original SP big contract which began trading in 1982.[22]
Like other indices managed by S&P Dow Jones Indices, but unlike indices such as the Russell 1000 Index which are strictly rule-based, the components of the S&P 500 index are selected by a committee. When considering the eligibility of a new addition, the committee assesses the company's merit using the following primary criteria:[3]
- Market capitalization - Market capitalization must be greater than or equal to US$18.0 billion.[23] These market cap eligibility criteria are for addition to an index, not for continued membership. As a result, an index constituent that appears to violate criteria for addition to that index is not removed unless ongoing conditions warrant an index change.[23]
- Market liquidity and public float – Annual dollar value traded to float-adjusted market capitalization is greater than 0.75.[24]
- Volume – Minimum monthly trading volume of 250,000 shares in each of the six months leading up to the evaluation date
- Stock exchange – Must be publicly listed on either the New York Stock Exchange (including NYSE Arca or NYSE American) or Nasdaq (Nasdaq Global Select Market, Nasdaq Select Market or the Nasdaq Capital Market).
- Domicile – The company must have its primary listing on a U.S. exchange, be subject to U.S. securities laws and derive at least 50% of its revenue in the U.S.[25]
- Securities that are ineligible for inclusion in the index are limited partnerships, master limited partnerships and their investment trust units, OTC Bulletin Board issues, closed-end funds, exchange-traded funds, Exchange-traded notes, royalty trusts, tracking stocks, preferred stock, unit trusts, equity warrants, convertible bonds, investment trusts, American depositary receipts, and American depositary shares.[3]
A stock may rise in value when it is added to the index since index funds must purchase that stock to continue tracking the index.[26][27]
In October 2021, Bloomberg News reported that a study alleged that some companies purchase ratings from S&P Global to increase their chances of entering the S&P 500 Index—even without meeting the full criteria for inclusion.[28]
Stock buyback
Dividends
Since its inception in 1926, the index's compound annual growth rate—including dividends—has been approximately 9.8% (6% after inflation), with the standard deviation of the return over the same time period being 20.81%.[29] While the index has declined in several years by over 30%,[30] it has posted annual increases 70% of the time,[31] with 5% of all trading days resulting in record highs.[32]
Returns are generally quoted as price returns (excluding returns from dividends). However, they can also be quoted as total return, which include returns from dividends and the reinvestment thereof, and "net total return", which reflects the effects of dividend reinvestment after the deduction of withholding tax.[2]
| Year | Change in Index | Total Annual Return, Including Dividends | Value of $1.00 Invested on January 1, 1970 | 5-Year Annualized Return | 10-Year Annualized Return | 15-Year Annualized Return | 20-Year Annualized Return | 25-Year Annualized Return |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1961 | 23.13% | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1962 | -11.81% | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1963 | 18.89% | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1964 | 12.97% | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1965 | 9.06% | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1966 | -13.09% | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1967 | 20.09% | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1968 | 7.66% | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1969 | -11.36% | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1970 | 0.10% | 4.01% | $1.04 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1971 | 10.79% | 14.31% | $1.19 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1972 | 15.63% | 18.98% | $1.41 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1973 | −17.37% | −14.66% | $1.21 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1974 | −29.72% | −26.47% | $0.89 | −2.35% | - | - | - | - |
| 1975 | 31.55% | 37.20% | $1.22 | 3.21% | - | - | - | - |
| 1976 | 19.15% | 23.84% | $1.51 | 4.87% | - | - | - | - |
| 1977 | −11.50% | −7.18% | $1.40 | −0.21% | - | - | - | - |
| 1978 | 1.06% | 6.56% | $1.49 | 4.32% | - | - | - | - |
| 1979 | 12.31% | 18.44% | $1.77 | 14.76% | 5.86% | - | - | - |
| 1980 | 25.77% | 32.50% | $2.34 | 13.96% | 8.45% | - | - | - |
| 1981 | −9.73% | −4.92% | $2.23 | 8.10% | 6.47% | - | - | - |
| 1982 | 14.76% | 21.55% | $2.71 | 14.09% | 6.70% | - | - | - |
| 1983 | 17.27% | 22.56% | $3.32 | 17.32% | 10.63% | - | - | - |
| 1984 | 1.40% | 6.27% | $3.52 | 14.81% | 14.78% | 8.76% | - | - |
| 1985 | 26.33% | 31.73% | $4.64 | 14.67% | 14.32% | 10.49% | - | - |
| 1986 | 14.62% | 18.67% | $5.51 | 19.87% | 13.83% | 10.76% | - | - |
| 1987 | 2.03% | 5.25% | $5.80 | 16.47% | 15.27% | 9.86% | - | - |
| 1988 | 12.40% | 16.61% | $6.76 | 15.31% | 16.31% | 12.17% | - | - |
| 1989 | 27.25% | 31.69% | $8.90 | 20.37% | 17.55% | 16.61% | 11.55% | - |
| 1990 | −6.56% | −3.10% | $8.63 | 13.20% | 13.93% | 13.94% | 11.16% | - |
| 1991 | 26.31% | 30.47% | $11.26 | 15.36% | 17.59% | 14.34% | 11.90% | - |
| 1992 | 4.46% | 7.62% | $12.11 | 15.88% | 16.17% | 15.47% | 11.34% | - |
| 1993 | 7.06% | 10.08% | $13.33 | 14.55% | 14.93% | 15.72% | 12.76% | - |
| 1994 | −1.54% | 1.32% | $13.51 | 8.70% | 14.38% | 14.52% | 14.58% | 10.98% |
| 1995 | 34.11% | 37.58% | $18.59 | 16.59% | 14.88% | 14.81% | 14.60% | 12.22% |
| 1996 | 20.26% | 22.96% | $22.86 | 15.22% | 15.29% | 16.80% | 14.56% | 12.55% |
| 1997 | 31.01% | 33.36% | $30.48 | 20.27% | 18.05% | 17.52% | 16.65% | 13.07% |
| 1998 | 26.67% | 28.58% | $39.19 | 24.06% | 19.21% | 17.90% | 17.75% | 14.94% |
| 1999 | 19.53% | 21.04% | $47.44 | 28.56% | 18.21% | 18.93% | 17.88% | 17.25% |
| 2000 | −10.14% | −9.10% | $43.12 | 18.33% | 17.46% | 16.02% | 15.68% | 15.34% |
| 2001 | −13.04% | −11.89% | $37.99 | 10.70% | 12.94% | 13.74% | 15.24% | 13.78% |
| 2002 | −23.37% | −22.10% | $29.60 | −0.59% | 9.34% | 11.48% | 12.71% | 12.98% |
| 2003 | 26.38% | 28.68% | $38.09 | −0.57% | 11.07% | 12.22% | 12.98% | 13.84% |
| 2004 | 8.99% | 10.88% | $42.23 | −2.30% | 12.07% | 10.94% | 13.22% | 13.54% |
| 2005 | 3.00% | 4.91% | $44.30 | 0.54% | 9.07% | 11.52% | 11.94% | 12.48% |
| 2006 | 13.62% | 15.79% | $51.30 | 6.19% | 8.42% | 10.64% | 11.80% | 13.37% |
| 2007 | 3.53% | 5.49% | $54.12 | 12.83% | 5.91% | 10.49% | 11.82% | 12.73% |
| 2008 | −38.49% | −37.00% | $34.09 | −2.19% | −1.38% | 6.46% | 8.43% | 9.77% |
| 2009 | 23.45% | 26.46% | $43.11 | 0.41% | −0.95% | 8.04% | 8.21% | 10.54% |
| 2010 | 12.78% | 15.06% | $49.61 | 2.29% | 1.41% | 6.76% | 9.14% | 9.94% |
| 2011 | -0.00% | 2.11% | $50.65 | −0.25% | 2.92% | 5.45% | 7.81% | 9.28% |
| 2012 | 13.41% | 16.00% | $58.76 | 1.66% | 7.10% | 4.47% | 8.22% | 9.71% |
| 2013 | 29.60% | 32.39% | $77.79 | 17.94% | 7.40% | 4.68% | 9.22% | 10.26% |
| 2014 | 11.39% | 13.69% | $88.44 | 15.45% | 7.67% | 4.24% | 9.85% | 9.62% |
| 2015 | −0.73% | 1.38% | $89.66 | 12.57% | 7.30% | 5.00% | 8.19% | 9.82% |
| 2016 | 9.54% | 11.96% | $100.38 | 14.66% | 6.94% | 6.69% | 7.68% | 9.15% |
| 2017 | 19.42% | 21.83% | $122.30 | 15.79% | 8.49% | 9.92% | 7.19% | 9.69% |
| 2018 | −6.24% | −4.38% | $116.94 | 8.49% | 13.12% | 7.77% | 5.62% | 9.07% |
| 2019 | 28.88% | 31.49% | $153.76 | 11.70% | 13.56% | 9.00% | 6.06% | 10.22% |
| 2020 | 16.26% | 18.40% | $182.06 | 15.22% | 13.89% | 9.88% | 7.47% | 9.56% |
| 2021 | 26.89% | 28.71% | $234.33 | 18.48% | 16.55% | 10.66% | 9.52% | 9.76% |
| 2022 | −19.44% | −18.11% | $191.89 | 9.43% | 12.56% | 8.80% | 9.80% | 7.64% |
| 2023 | 24.23% | 26.29% | $242.34 | 15.69% | 12.03% | 13.97% | 9.69% | 7.56% |
| High | 34.11% | 37.58% | --- | 28.56% | 19.21% | 18.93% | 17.88% | 17.25% |
| Low | −38.49% | −37.00% | --- | −2.35% | −1.38% | 4.24% | 5.62% | 7.56% |
| Median | 12.36% | 15.43% | --- | 14.02% | 12.56% | 10.71% | 11.34% | 10.40% |
| Year | Change in Index | Total Annual Return, Including Dividends | Value of $1.00 Invested on 1970‑01‑01 | 5-Year Annualized Return | 10-Year Annualized Return | 15-Year Annualized Return | 20-Year Annualized Return | 25-Year Annualized Return |
- Valetkevitch, Caroline (May 6, 2013). "Key dates and milestones in the S&P 500's history". Reuters.
- "S&P U.S. Indices Methodology" (PDF). S&P Global. Retrieved October 21, 2023.
- "S&P 500". Encyclopædia Britannica. March 14, 2024.
- "S&P 500 Index grew over $6.7 trillion in one year to January 2024, finds GlobalData". GlobalData. February 16, 2024.
- "S&P 500®" (PDF). S&P Global.
- S&P Dividend Aristocrats Indices Methodology (PDF) (Report). S&P Dow Jones Indices. September 1, 2023. p. 4. Archived (PDF) from the original on November 23, 2023. Retrieved November 28, 2023.
- Preston, Hamish (June 9, 2020). "Higher Turnover Ahead For S&P 500? Not Necessarily!". S&P Global.
- Wathen, Jordan (April 9, 2019). "How Are S&P 500 Stocks Chosen?". The Motley Fool.
- Chang, Ellen (June 28, 2019). "7 S&P Index Funds to Buy Now". U.S. News & World Report.
- Thune, Kent. "The Best S&P 500 Index Funds". The Balance. Archived from the original on June 3, 2023. Retrieved November 28, 2023.
- Riggs, Thomas, ed. (2015). "Standard & Poor's". Gale Encyclopedia of U.S. Economic History. Vol. 3 (2nd ed.). Gale. p. 1256. Gale CX3611000855.
- Duggan, Wayne (June 13, 2019). "This Day In Market History: S&P 500 Quotes Delivered Every 15 Seconds". Benzinga.
- "S&P Dow Jones Indices Announces Update to S&P Composite 1500 Market Cap Guidelines" (PDF). S&P Global. April 1, 2024. Retrieved April 8, 2024.
- "S&P Dow Jones Indices Announces Update to S&P Composite 1500 Market Cap Guidelines" (PDF). January 4, 2022. Retrieved January 5, 2022.
- Krantz, Matt (July 5, 2013). "Do stocks soar if they get into the S&P 500?". USA TODAY.
- Lee, Justina (October 12, 2021). "S&P 500 Membership May Be 'For Sale,' NBER Research Suggests". Bloomberg. Retrieved January 21, 2022.
- "S&P 500 Standard Deviation". Quantamental Finance. Pie-R-Cube. August 13, 2021. Archived from the original on January 23, 2022. Retrieved May 14, 2023.
- Santoli, Michael (June 18, 2017). "The S&P 500 has already met its average return for a full year, but don't expect it to stay here". CNBC.
- Carlozo, Lou (October 2, 2018). "Why Investors Love the S&P 500". U.S. News & World Report.
- Carlson, Ben (February 27, 2020). "Worried about the stock market? Resist the urge to panic". Fortune.