Runcination_(geometry)
In geometry, runcination is an operation that cuts a regular polytope (or honeycomb) simultaneously along the faces, edges, and vertices, creating new facets in place of the original face, edge, and vertex centers.[citation needed]
This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. (March 2015) |
It is a higher order truncation operation, following cantellation, and truncation.
It is represented by an extended Schläfli symbol t0,3{p,q,...}. This operation only exists for 4-polytopes {p,q,r} or higher.
This operation is dual-symmetric for regular uniform 4-polytopes and 3-space convex uniform honeycombs.
For a regular {p,q,r} 4-polytope, the original {p,q} cells remain, but become separated. The gaps at the separated faces become p-gonal prisms. The gaps between the separated edges become r-gonal prisms. The gaps between the separated vertices become {r,q} cells. The vertex figure for a regular 4-polytope {p,q,r} is an q-gonal antiprism (called an antipodium if p and r are different).
For regular 4-polytopes/honeycombs, this operation is also called expansion by Alicia Boole Stott, as imagined by moving the cells of the regular form away from the center, and filling in new faces in the gaps for each opened vertex and edge.
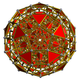
Runcinated 4-polytopes/honeycombs forms: